√ p(x) meaning statistics 205198-What does p= mean in statistics
X represents the random variable X P (X) represents the probability of X P (X = x) refers to the probability that the random variable X is equal to a particular value, denoted by x As an example, P (X = 1) refers to the probability that the random variable X is equal to 1So if a data set has 10 values, the sum of the 10 values must equal the mean x 10 If the mean of the 10 values is 35 (you could pick any number), this constraint requires that the sum of the 10 values must equal 10 x 35 = 35 With that constraint, the first value in the data set is free to varyThe mean is the Sum of (X × P(X)) μ = 36 The variance is the Sum of (X 2 × P(X)) minus Mean 2 Variance

Lesson Plan Statistics And Probability Cot 3 Variance Standard Deviation
What does p= mean in statistics
What does p= mean in statistics-The negative coefficient indicates that for every oneunit increase in X, the mean of Y decreases by the value of the coefficient () Your pvalue is displayed using scientific notation You need to move the decimal point to the left 15 places, which produces a very, very small pvalueIn general, capital letters refer to population attributes (ie, parameters);



Variance Wikipedia
The term 'µ' represents the mean number of the successes that has occurred in a specific regionA very small pvalue means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis Reporting pvalues of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields Since the precise meaning of pvalue is hard to grasp, misuse is widespread and has been a major topic in metascienceThe mean and variance for the approximately normal distribution of X are np and np(1p), identical to the mean and variance of the binomial(n,p) distribution Similarly, the mean and variance for the approximately normal distribution of the sample proportion are p and (p(1p)/n)
The term 'µ' represents the mean number of the successes that has occurred in a specific regionIn statistical hypothesis testing, the pvalue or probability value is, for a given statistical model, the probability that, when the null hypothesis is true, the statistical summary (such as the absolute value of the sample mean difference between two compared groups) would be greater than or equal to the actual observed resultsIn statistics, the pvalue is the probability of obtaining results at least as extreme as the observed results of a statistical hypothesis test, assuming that the null hypothesis is correct
Understanding and calculating standard deviation Published on September 17, by Pritha Bhandari Revised on January 21, 21 The standard deviation is the average amount of variability in your dataset It tells you, on average, how far each value lies from the mean A high standard deviation means that values are generally far from the mean, while a low standard deviation indicates that1 Introduction to Statistics Lecture 16 Reminder Quiz 3 next week Binomial model (cont'd) For n random Bernoulli trials, X is the number of successes If the probability of success is p, q=1p is the probability ofBASIC STATISTICS 1 SAMPLES,RANDOMSAMPLING ANDSAMPLESTATISTICS 11 Random Sample The random variables X1,X2,, are called a random sample of size n fromthe populationf(x)if X1,X2,, are mutuallyindependent random variablesand themar ginal probability density function of each Xi is the same function of f(x) Alternatively, X1,X2,, are called independent and identically
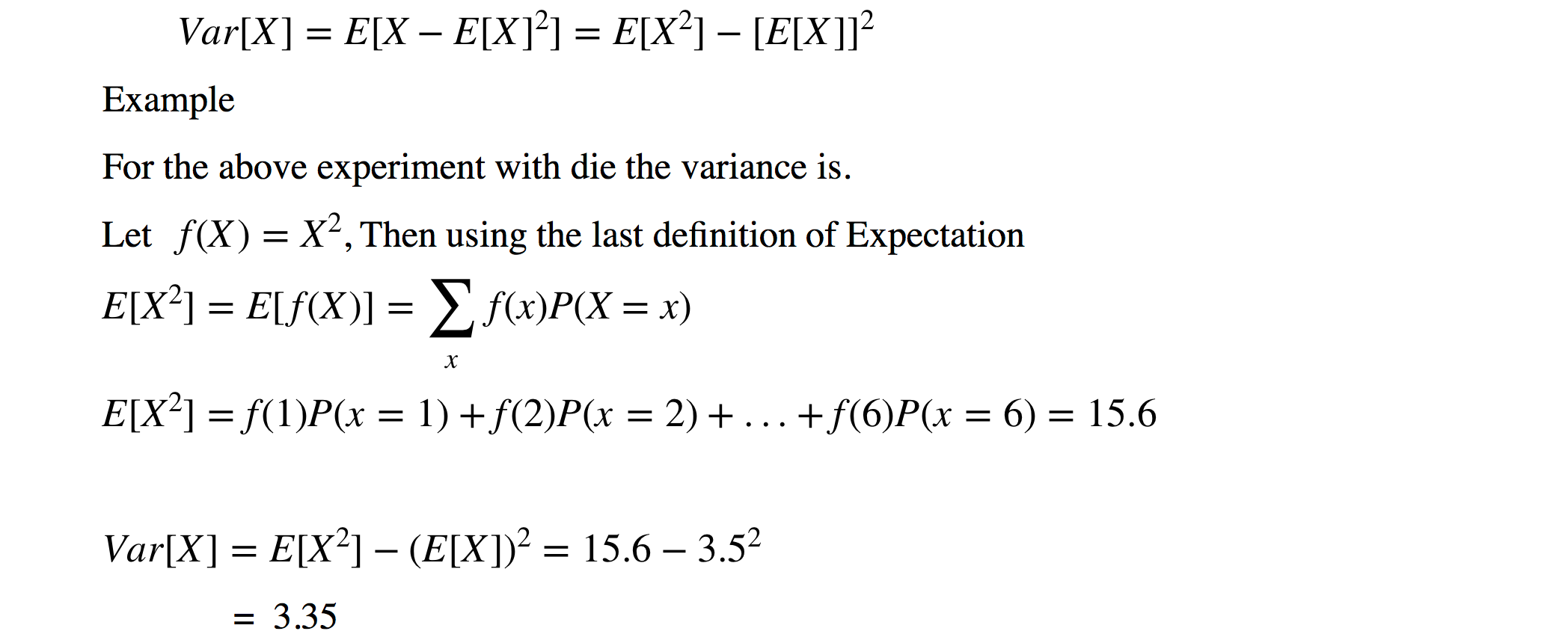


Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science
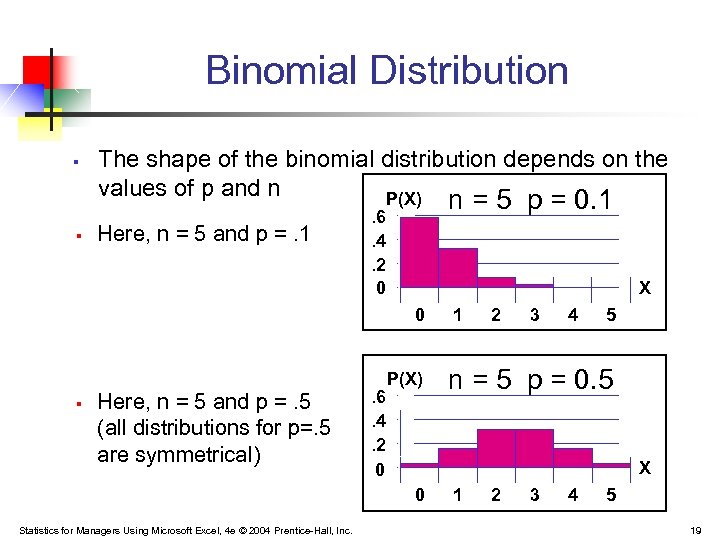


Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel 4 Th
This video explains how to use the pvalue to draw conclusions from statistical output Try the quiz after https//youtube/Po9E7tfwMYsThis video includesAlgebra > Probabilityandstatistics> SOLUTION The mean and variance of a Binomial variable X with parameters n and p are 16 and 8Find P(X1) and P(X>2) Log OnGlossary of Statistical Terms You can use the "find" (find in frame, find in page) function in your browser to search the glossary



Using R For Introductory Statistics Chapter 5 R Bloggers


Http Eschool2 Bsd7 Org Mod Resource View Php Id 069
English Phrases Written Mathematically When the English says Interpret this as X is at least 4 X ≥ 4 The minimum of X is 4 X ≥And lowercase letters refer to sample attributes (ie, statistics) For example, P refers to a population proportion;In null hypothesis significance testing, the pvalue is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the results actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct A very small pvalue means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis Reporting pvalues of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields Since the precise meaning of pvalue is hard to grasp, misuse



Lesson Plan Statistics And Probability Cot 3 Variance Standard Deviation


2
Click here to see ALL problems on Probabilityandstatistics Question what is p(x 84), when mean is 100 and standard deviation is 8 Answer by stanbon(757) ( Show Source )In statistical hypothesis testing, the pvalue or probability value is, for a given statistical model, the probability that, when the null hypothesis is true, the statistical summary (such as the absolute value of the sample mean difference between two compared groups) would be greater than or equal to the actual observed resultsAnd p, to a sample proportion X refers to a set of population elements;


2



Statistics Symbols Cheat Sheet Docsity
The expected value (or mean) of X, where X is a discrete random variable, is a weighted average of the possible values that X can take, each value being weighted according to the probability of that event occurring The expected value of X is usually written as E(X) or m E(X) = S x P(X = x) So the expected value is the sum of (each of the possible outcomes) × (the probability of theFormal Definition Like many mathematical terms, there's the informal definition (given above), and then there's the formal one The probability mass function, f(x) = P(X = x), of a discrete random variable X has the following properties All probabilities are positive fx(x) ≥ 0Definition 31 (Estimation) Estimation is the process of infering or attempting to guess the value of one or several population parameters from a sample Therefore, an estimator \(\hat\theta\) of a parameter \(\theta\in\Theta\) is an statistic with range in the parameter space \(\Theta\)


2


2
A very small pvalue means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis Reporting pvalues of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields Since the precise meaning of pvalue is hard to grasp, misuse is widespread and has been a major topic in metascienceP(78 < x < ) = P(2 < z < 1) = 1587 – 0228 = 1359 Final Solution Therefore, the Probability that a single student will get a score between 4 and 78 is 1359 or about 135% This makes sense because the mean is and by the Empirical Rule, over 68% of the students will score between 78 and 86The expected value (or mean) of X, where X is a discrete random variable, is a weighted average of the possible values that X can take, each value being weighted according to the probability of that event occurring The expected value of X is usually written as E(X) or m E(X) = S x P(X = x) So the expected value is the sum of (each of the possible outcomes) × (the probability of the


Nanopdf Com Download Chapter 7 Random Variables Pdf



Binomial A Binomial Random Variable Is The Number Of Successes X In N Repeated Trials Of A Binomial Experiment Binomial Formula Http Stattrek Com Probability Distributions Binomial Aspx X The Number Of Successes That Result From The Binomial Experiment
In statistics, percentiles are used to understand and interpret data The nth percentile of a set of data is the value at which n percent of the data is below it In everyday life, percentiles are used to understand values such as test scores, health indicators, and other measurements For example, an 18yearold male who is six and a half feet tall is in the 99th percentile for his heightJoint Probability A joint probability is a statistical measure where the likelihood of two events occurring together and at the same point in time are calculated Joint probability is thePvalue Formula We Know that Pvalue is a statistical measure, that helps to determine whether the hypothesis is correct or not Pvalue is a number that lies between 0 and 1 The level of significance(α) is a predefined threshold that should be set by the researcher It is generally fixed as 005 The formula for the calculation for Pvalue is



Statistics Mean Value And Net Revenue Mathematics Stack Exchange



Ap Statistics Test 7 Chapter 7 Edventure Ga
And n, to sample sizeThe term 'p' represents the probability of getting success from the 'n' binomial trials The poisson formula is represented by the statistical formula as P(x;µ)=(eµ)(µx)/x!Probability distribution definition and tables In probability and statistics distribution is a characteristic of a random variable, describes the probability of the random variable in each value Each distribution has a certain probability density function and probability distribution function


Rstudio Pubs Static S3 Amazonaws Com 580ffce4942ac7e19ea763c9869 Html
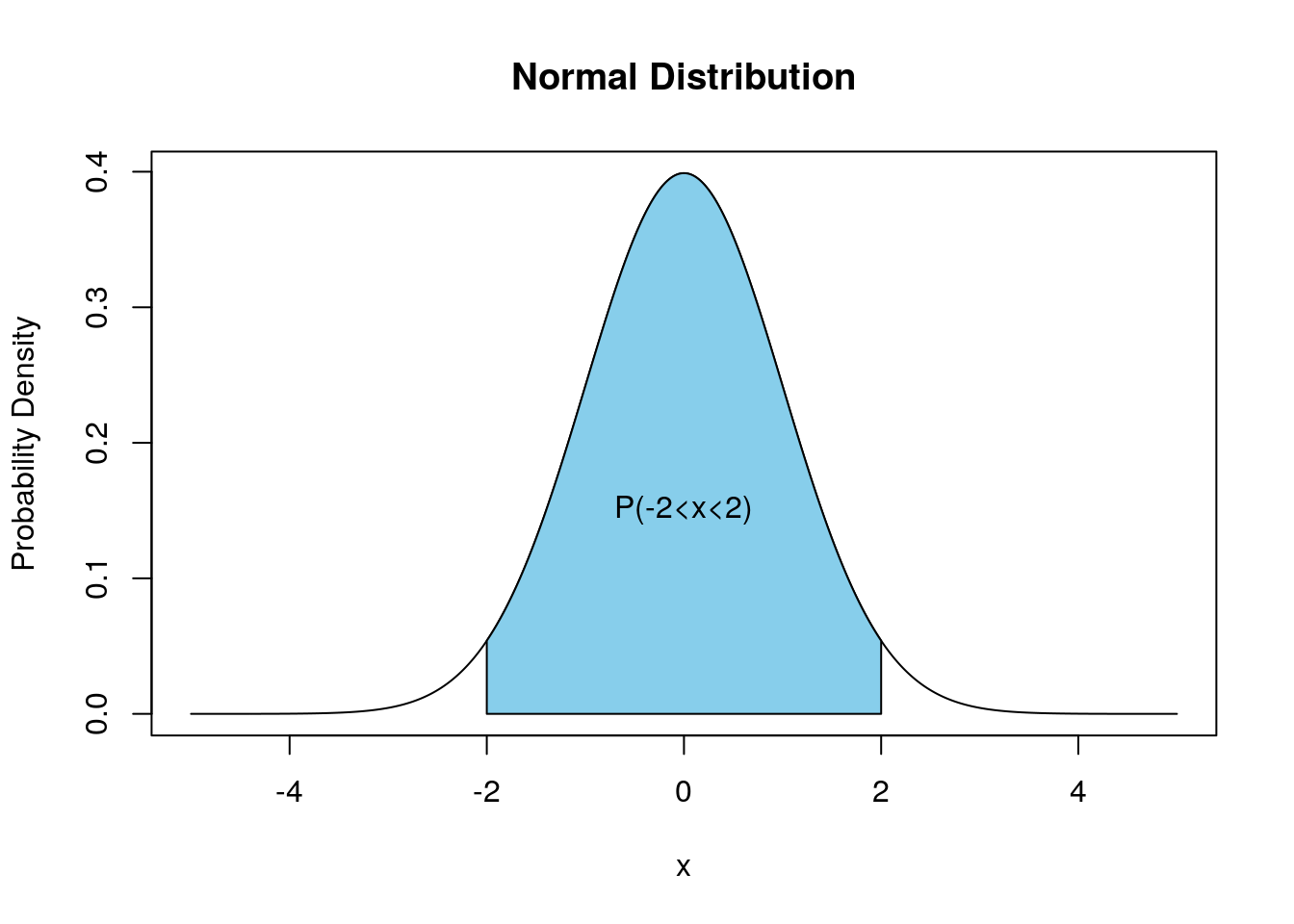


Chapter 8 Continuous Random Variables Introduction To Statistics And Data Science
F(x) = P(X≤ x) μ population mean mean of population values μ = 10 E(X) expectation value expected value of random variable X E(X) = 10 E(X Y) conditional expectation expected value of random variable X given Y E(X Y=2) = 5 var(X) variance variance of random variable X var(X) = 4 σ 2 variance variance of population values σ 2 = 4 std(X) standard deviationX = Normal random variable, ie, X ~ N ( miu, stdev**2 ) miu = mean of normal distribution stdev = standard deviation of normal distribution x = number of successful outcome P(X < x) = 05 * ( 1 erf( (xmiu)/(stdev * 2**05) ) ) Note P(X = x) = 0 for continuous probability distribution function P( a < X < b ) = P(X < b) ─ P(X < a) Example 6 The time taken to assemble a car is normallyThe mean and variance for the approximately normal distribution of X are np and np(1p), identical to the mean and variance of the binomial(n,p) distribution Similarly, the mean and variance for the approximately normal distribution of the sample proportion are p and (p(1p)/n)
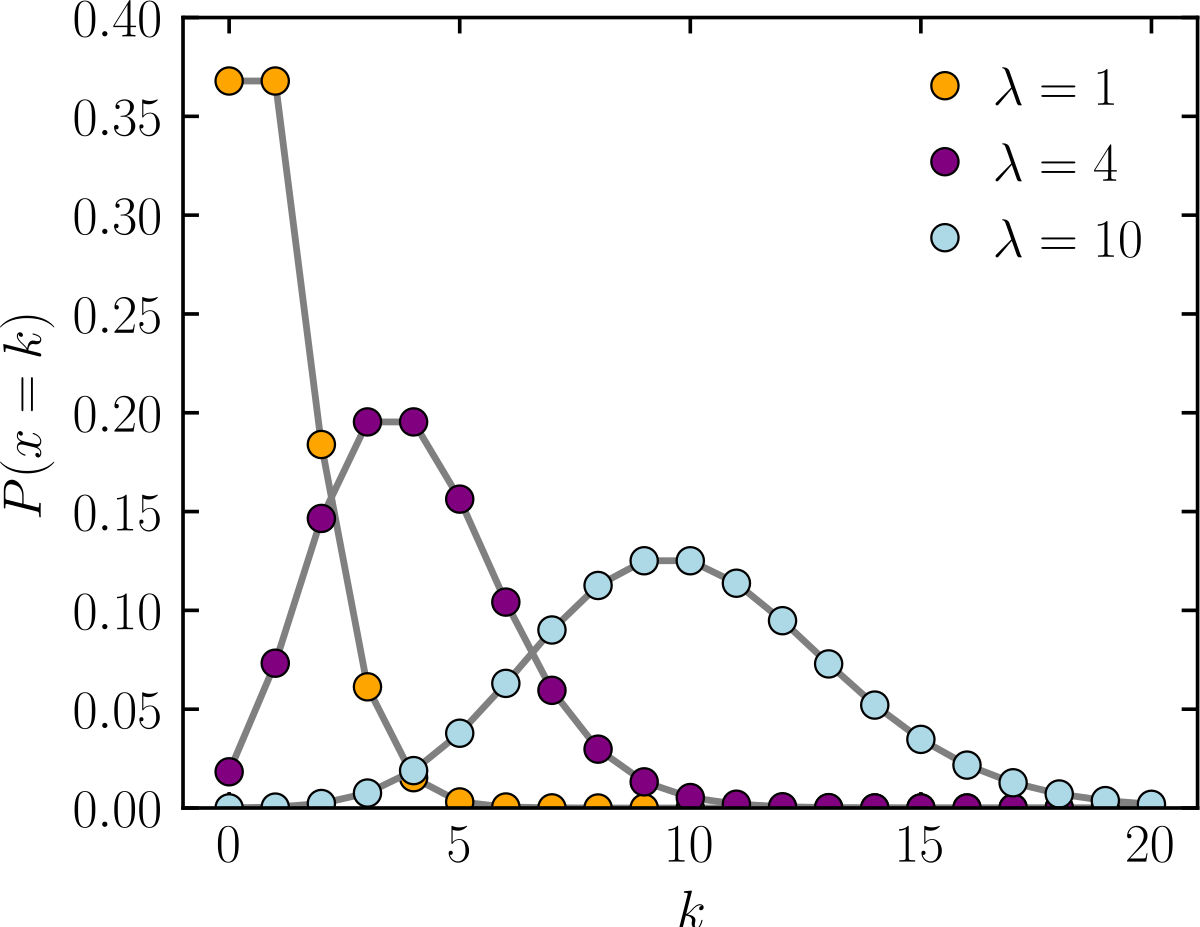


Poisson Distribution Wikipedia
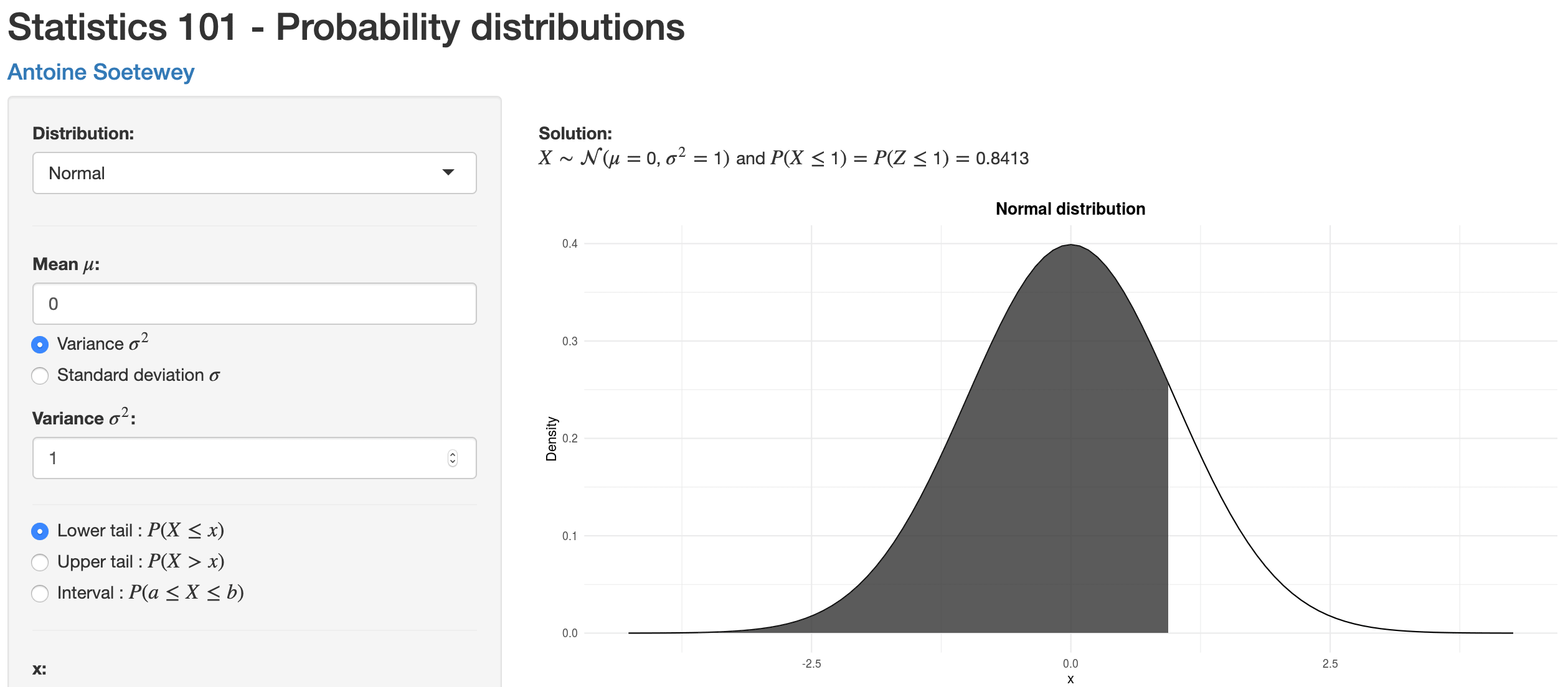


A Guide On How To Read Statistical Tables Stats And R
The mean is the Sum of (X × P(X)) μ = 36 The variance is the Sum of (X 2 × P(X)) minus Mean 2 VarianceLearn how to compare a Pvalue to a significance level to make a conclusion in a significance test Given the null hypothesis is true, a pvalue is the probability of getting a result as or more extreme than the sample result by random chance alone If a pvalue is lower than our significance level, we reject the null hypothesis If not, we fail to reject the null hypothesisList of common statistics formulas (equations) used in descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and survey sampling Includes links to web pages that explain how to use the formulas, including sample problems with solutions



Probability Basic Concepts And Random Variables Sage Research Methods
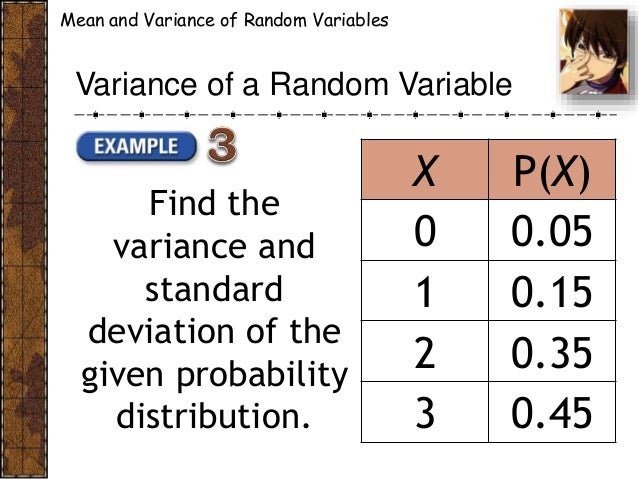


Cabt Shs Statistics Probability Expected Value And Variance Of Di
List of common statistics formulas (equations) used in descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and survey sampling Includes links to web pages that explain how to use the formulas, including sample problems with solutionsPValues The other number that is part of a test of significance is a pvalue A pvalue is also a probability, but it comes from a different source than alpha Every test statistic has a corresponding probability or pvalue This value is the probability that the observed statistic occurred by chance alone, assuming that the null hypothesisIn statistics, percentiles are used to understand and interpret data The nth percentile of a set of data is the value at which n percent of the data is below it In everyday life, percentiles are used to understand values such as test scores, health indicators, and other measurements For example, an 18yearold male who is six and a half feet tall is in the 99th percentile for his height



Engineering Statistics Lab 2 Chapter 3 Material Using Minitab To Plot Frequency Distribution And Calculate Mea Homeworklib



Statistics Chapter 7 Quiz Flashcards Quizlet
\μ=∑(x∙P(x))\nonumber\ The standard deviation, Σ, of the PDF is the square root of the variance \σ=\sqrt{∑(x – μ)2 ∙ P(x)}\nonumber\ When all outcomes in the probability distribution are equally likely, these formulas coincide with the mean and standard deviation of the set of possible outcomesSo if a data set has 10 values, the sum of the 10 values must equal the mean x 10 If the mean of the 10 values is 35 (you could pick any number), this constraint requires that the sum of the 10 values must equal 10 x 35 = 35 With that constraint, the first value in the data set is free to varyVar(X) = p – p2 = p*(1p) Binomial distribution It is a probability distribution that concludes the value that takes one of two independent values under a set of assumptions or parameters



Ap Statistics Sampling Distribution Of Mean Name Suppose That We



University Statistics Probability Distribution Getting The Mean And Standard Deviation Homeworkhelp
The point estimate of your confidence interval will be whatever statistical estimate you are making (eg population mean, the difference between population means, proportions, variation among groups) Example Point estimate In the TVwatching example, the point estimate is the mean number of hours watched 35 Finding the critical valueThe mean value of "x" is obtained from repeated observations of the value of "x" To calculate xbar, observe the value of "x" n times Then, add all of the observed values of "x" and divide the sum by n The resulting quantity is the mean value of "x," the xbarAnd x, to a set of sample elements N refers to population size;



Applied Statistics The Poisson Probability Distribution Function Mean And Variance


Faculty Math Illinois Edu Hildebr 370 408discrete1 Pdf
In Statistics, the probability distribution gives the possibility of each outcome of a random experiment or events It provides the probabilities of different possible occurrence Also read, events in probability, here To recall, the probability is a measure of uncertainty of various phenomenaLike, if you throw a dice, what the possible outcomes of it, is defined by the probabilityP robability and statistics correspond to the mathematical study of chance and data, respectively The following reference list documents some of the most notable symbols in these two topics, along with each symbol's usage and meaning For readability purpose, these symbols are categorized by function into tables Other comprehensive lists of math symbols — as categorized by subject andThe term 'p' represents the probability of getting success from the 'n' binomial trials The poisson formula is represented by the statistical formula as P(x;µ)=(eµ)(µx)/x!



Solved Daily Newspapers A Survey Was Taken Of The
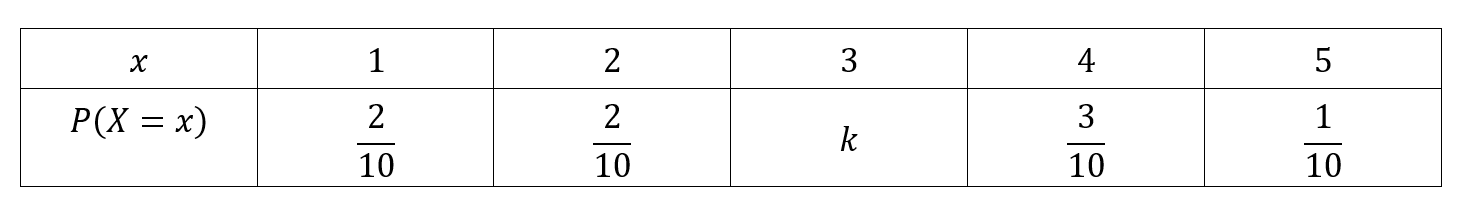


Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables


Q Tbn And9gcrkubyxuotg9n Utduxlsgstwkruyxablfekpl94nxy4paxu6hb Usqp Cau



Chapter 5 Probability And Statistics Pdf Document



Statistics Wikiwand


2


Projecteuclid Org Download Pdf 1 Euclid Aos


Dornsife Usc Edu Assets Sites 1185 Docs 541 Hw 541a S18 Pdf



Variance Wikipedia


The Z Score Statistics


Www Artsci Uc Edu Content Dam Refresh Artsandsciences 62 Departments Math Docs Stats Qualifying Exam Aug 16 Pdf



Statistics Recap


Http Www Stat Yale Edu Hz68 242 Hw1 Pdf



Kirk Borne 10 Page Pdf Datascience Cheat Sheet Covers Concepts In Statistical Learning Machinelearning Deeplearning Probability Statistics Bigdata Frameworks Sql Etc T Co Jfnkndlt5y Ai Datascientists



Ti Or Ti 84 Calculator Instructions For Statistics To Enter Data Into



2nd Puc Statistics Question Bank Chapter 5 Theoretical Distribution Kseeb Solutions
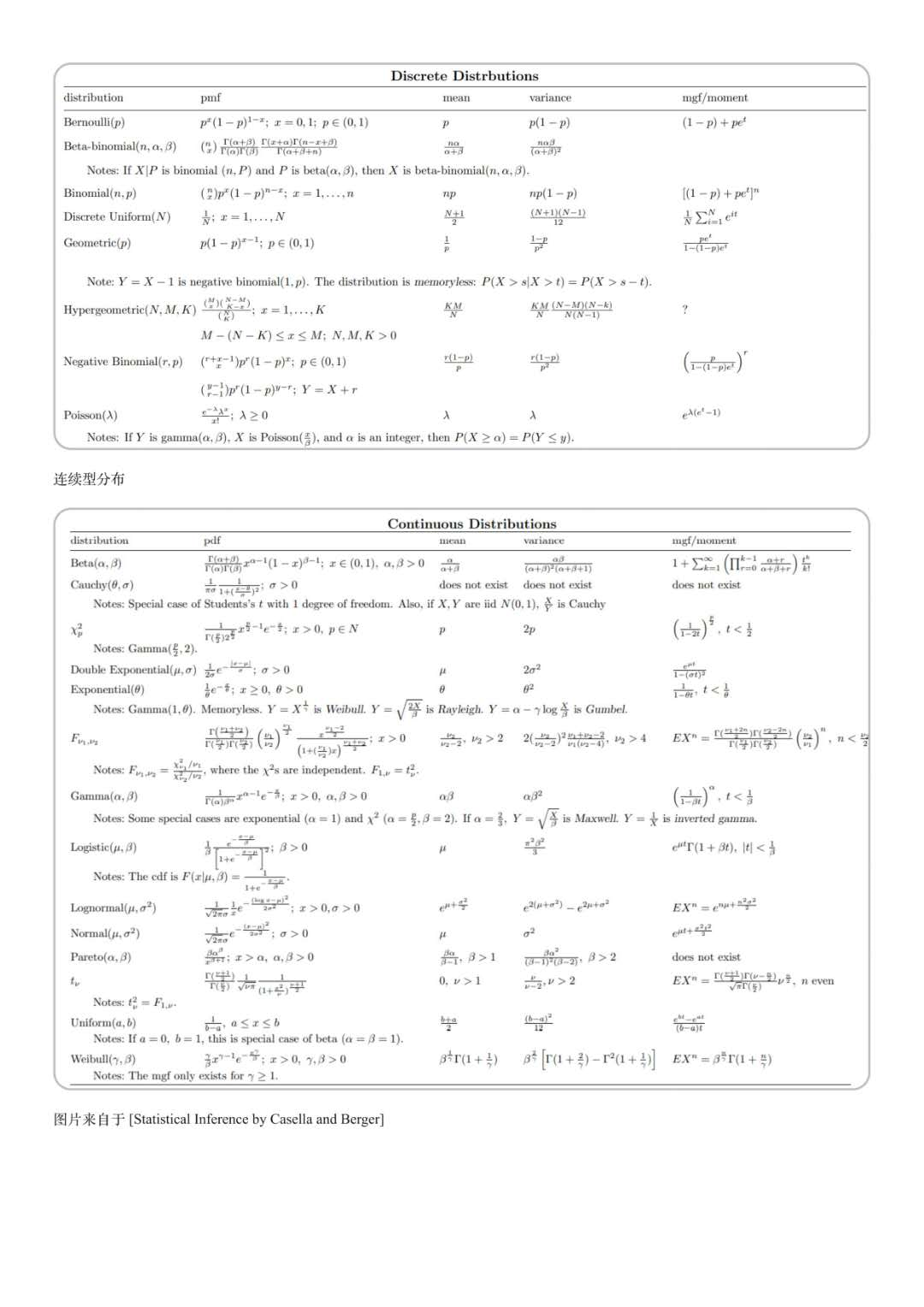


Basic Method Of Data Mining Probability And Statistics 3 Common Distribution And Hypothesis Test



Statistics Archives Www Tinspireapps Com Blog



Null Null Manualzz



Example Transforming A Discrete Random Variable Video Khan Academy


Dornsife Usc Edu Assets Sites 1185 Docs 408 Hw 408 F Pdf


Cs Nyu Edu Roweis Notes Mlss05 Pdf


Statistics Lab 3 Normal Distribution Probabilities
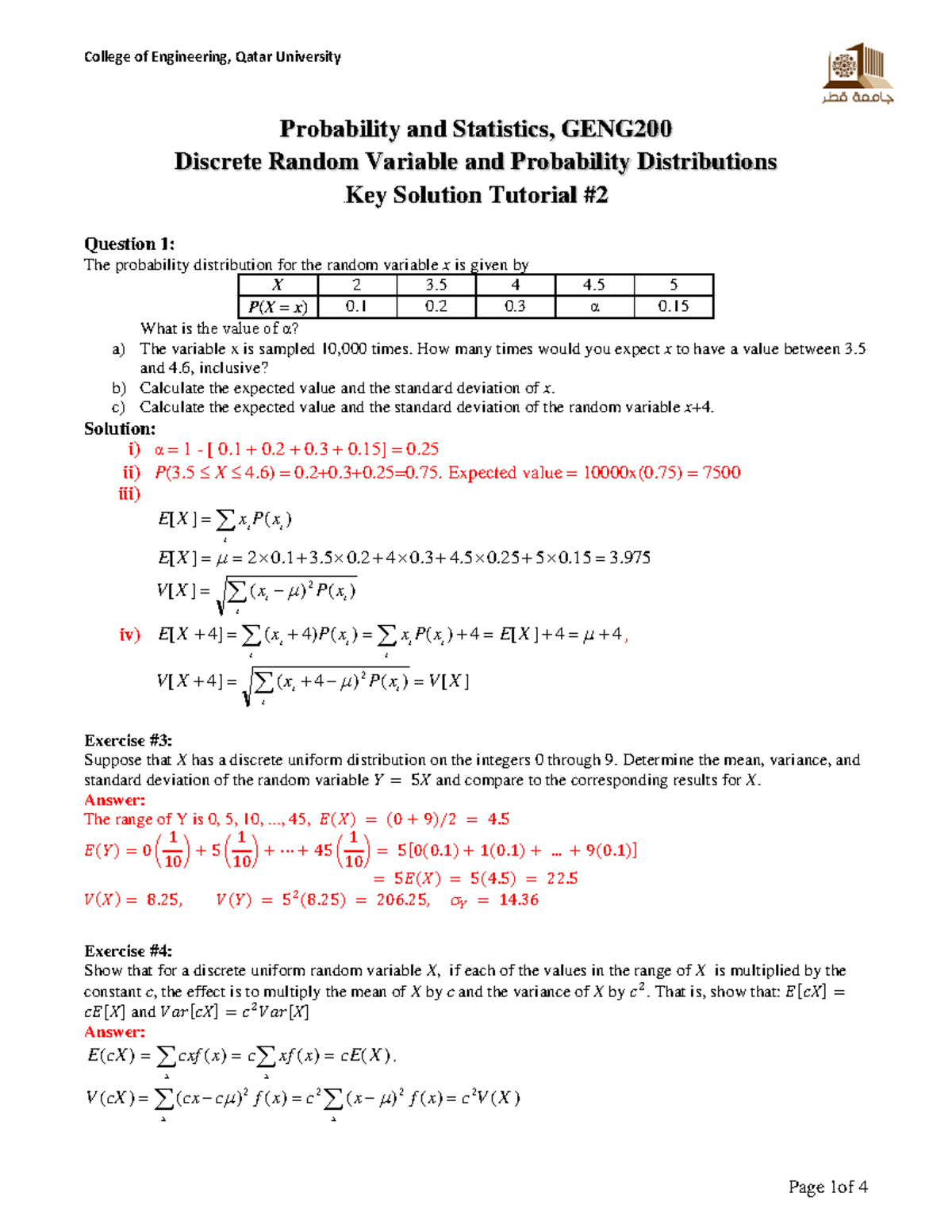


Fall 19 Tutorial 2 Chap 3 Solution Probability And Statistics Geng Discrete Random Variable And Probability Distributions Key Solution Tutorial Question The Studocu



Examination In Probability Theory And Statistics Variant 9 1 Discrete Distribution For X Is Given By Homeworklib



7 1 7 2 Take Home Doc Ap Statistics Chapter 7 Take Home Assignment Mean And Variance Of Random Variables Practice Name 1 Determine Whether The Course Hero


2
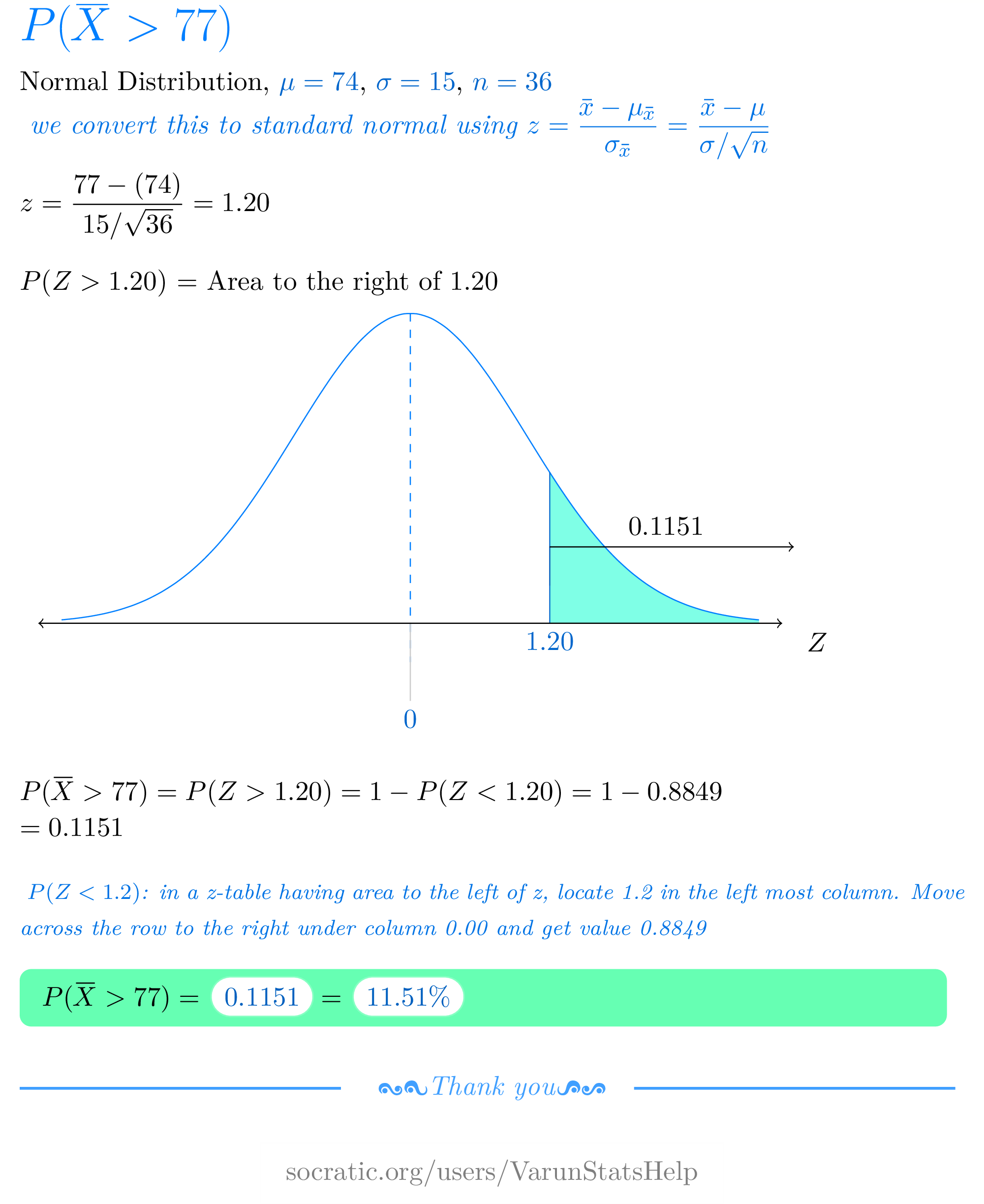


The Distribution Of Scores For The Third Exam In A Statistics Course Has A Mean Of 74 And A Standard Deviation Of 15 A Random Sample Of 36 Exam Papers Is Selected
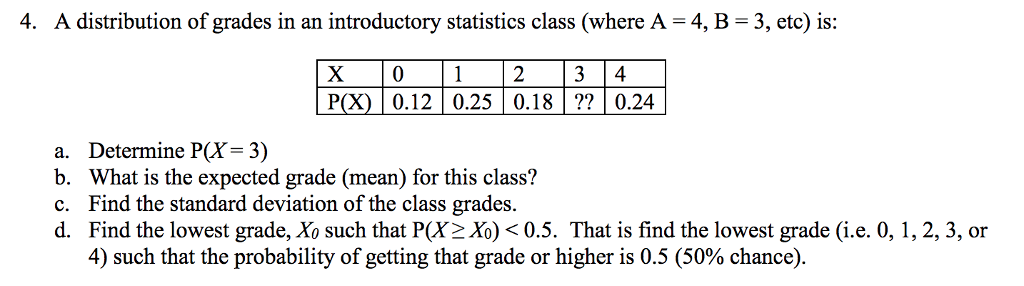


Solved 4 A Distribution Of Grades In An Introductory Sta Chegg Com


Http Www Livingston Org Cms Lib4 Nj Centricity Domain 713 Chapter 7 Take Home Test Pdf



Mean Variance And St Deviation For Discrete Random Variable Ti Nspire Youtube



Math1238 Tutorial 4 1 Tute 4 1 Math1238 Statistics Epidemiology Name Student Number All Students Must Complete This Section A Pathologist Working In Course Hero


Http Www Users Wfu Edu Ecarlson Skeptic Statistics Pdf


Q Tbn And9gcr8eiry5i6fjkrn3asviqugb50j6vhc03jo8tnxwqex4qy3la2z Usqp Cau


Http Staff Katyisd Org Sites Publishingimages Pages Documents Chapter 7 random variables hw answer key Pdf


Statext Android App Statistics Study


2
/p-val-0495f383de964788b560dd11c833a152.png)


P Value Definition


Binomial Distribution Video Khan Academy



Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science



The Normal Distribution Business Statistics Uiowa Wiki
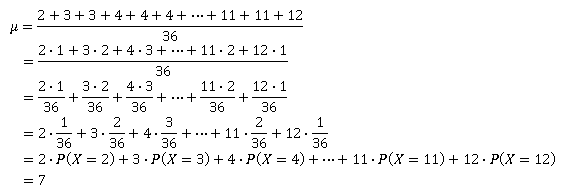


Chapter 6



Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables Statistics For Science Env Ppt Download



1 3 6 6 18 Binomial Distribution
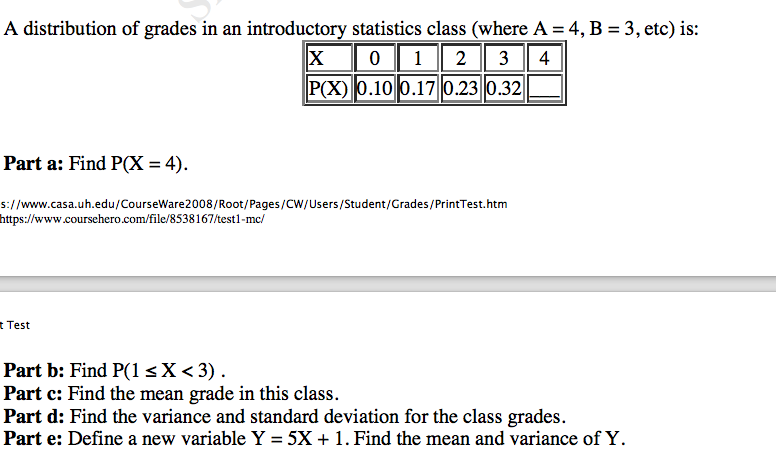


Solved A Distribution Of Grades In An Introductory Statis Chegg Com


Cpb Us E1 Wpmucdn Com Sites Pc Gsu Edu Dist 8 175 Files 15 07 8 1faq 0001 2hwyvnx Pdf



Statistical Analysis Made Easy With These Awesome Calculators



Chapter 5 Answers Business Statistics Studocu


Http Media Rochester K12 Mi Us Download Token Ocarojcyvwc 3d
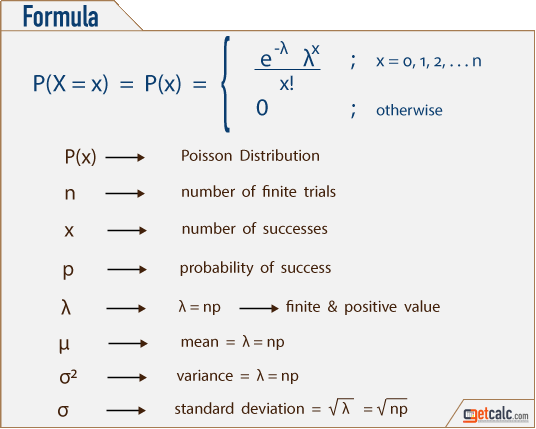


Poisson Distribution Calculator Formula Examples



Solution To Practice Midterm 2 Department Of Statistics And
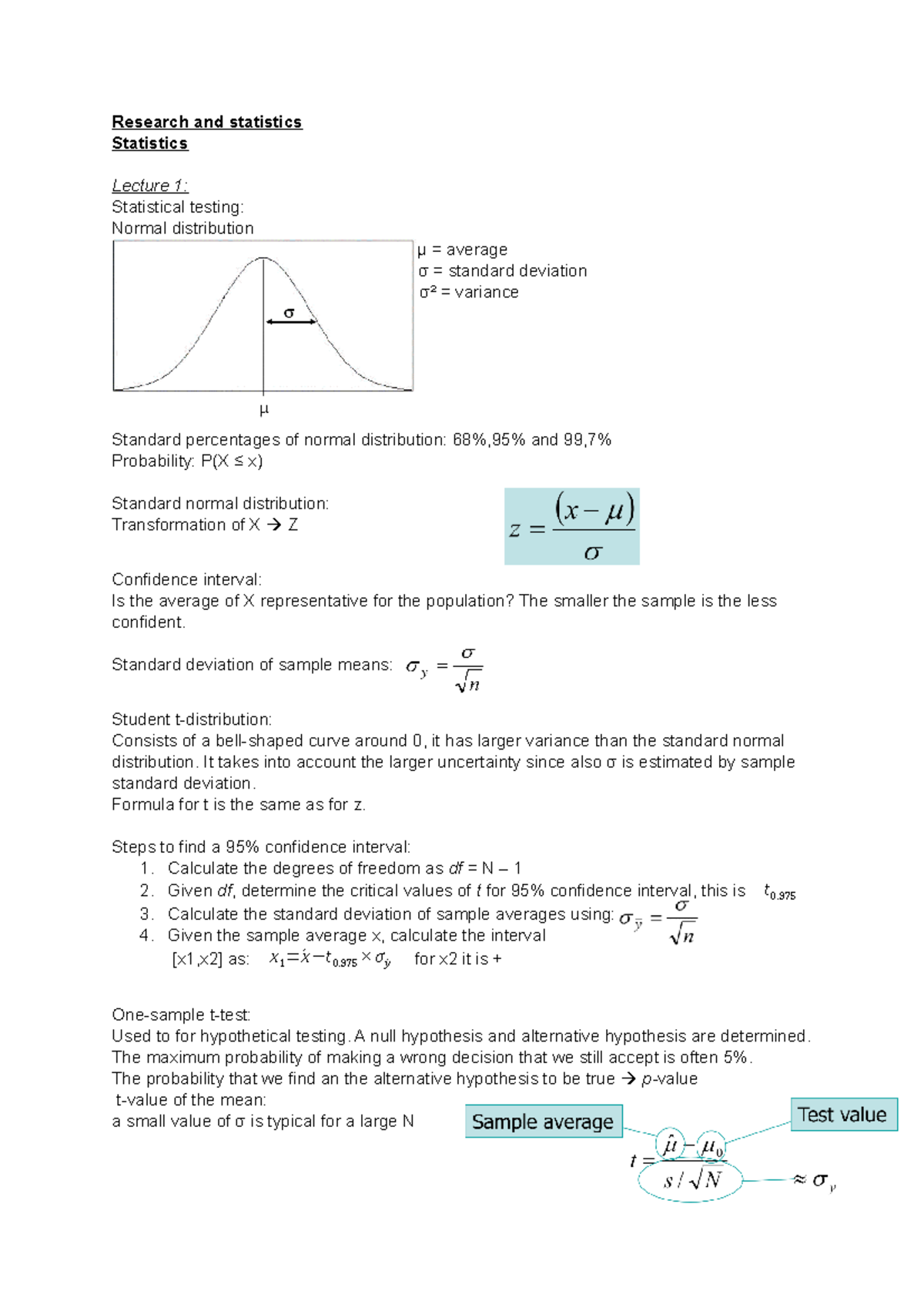


Statistics Summary 7u9x0 Studeersnel


Answer In Statistics And Probability For Caroline
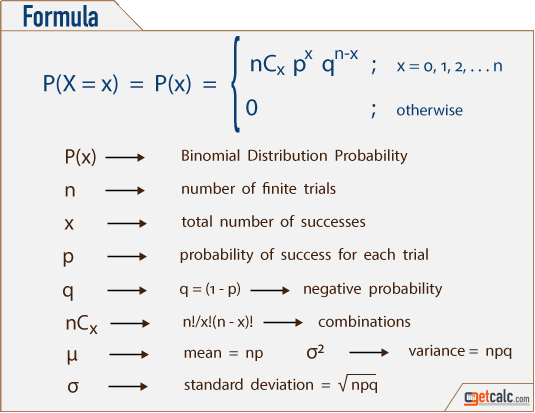


Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator


Www Math Uh Edu Bekki 3339fa16 Notes 3339day14 Done Pdf


3


2



Solution Probability And Statistics 2 Studypool


Www Manhassetschools Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 116 Dataid Filename Ap stats aim 43 binomial mean and sd Pdf



Consider A Normal Distribution With Mean 33 And Standard Deviation 9 What Is The Probability A Value Selected At Ra Statistics Math Probability Math Math Help



Help Online Origin Help Statistics On Columns



Discrete Probability Distributions



Solved Complete The Following Probability Distrib



Probability Basic Concepts And Random Variables Sage Research Methods


Www3 Nd Edu Dgalvin1 S09 S09e2prac Sols Pdf



12 Questions On Probability And Statistics Theory Exam 1 Stat 160b Docsity


Characterizing A Distribution Introduction To Statistics 6 4 Documentation


2



6 1 Hw Ws



Firm Heterogeneity S And Statistics Of Price P 0 Price Variance Download Scientific Diagram


2


Wwphs Sharpschool Com Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid



Applied Statistics Mean And Variance Of Binomial Distribution
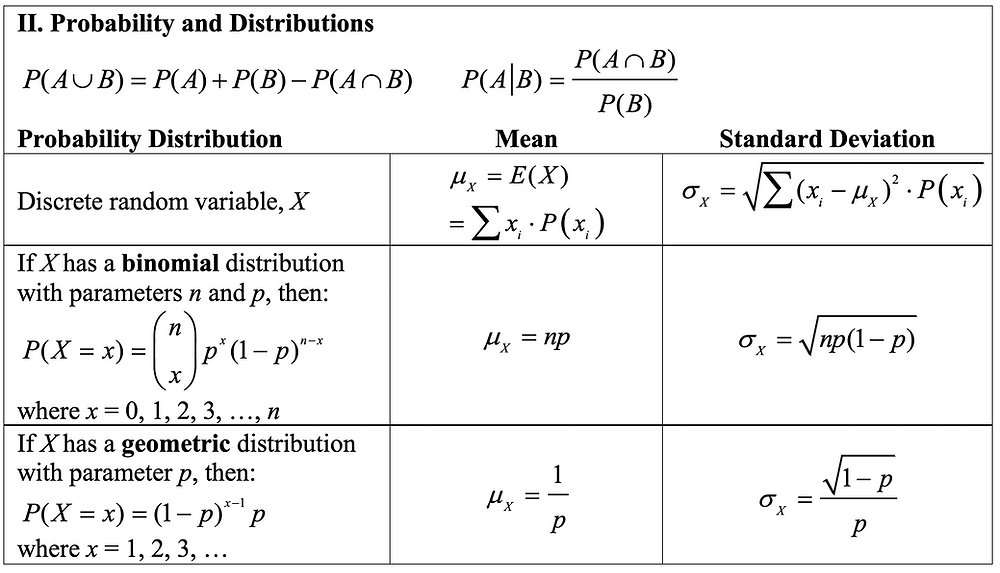


A New Formula Sheet For The Ap Statistics Exam
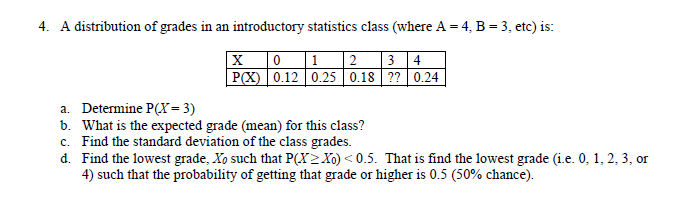


Solved 4 A Distribution Of Grades In An Introductory Sta Chegg Com
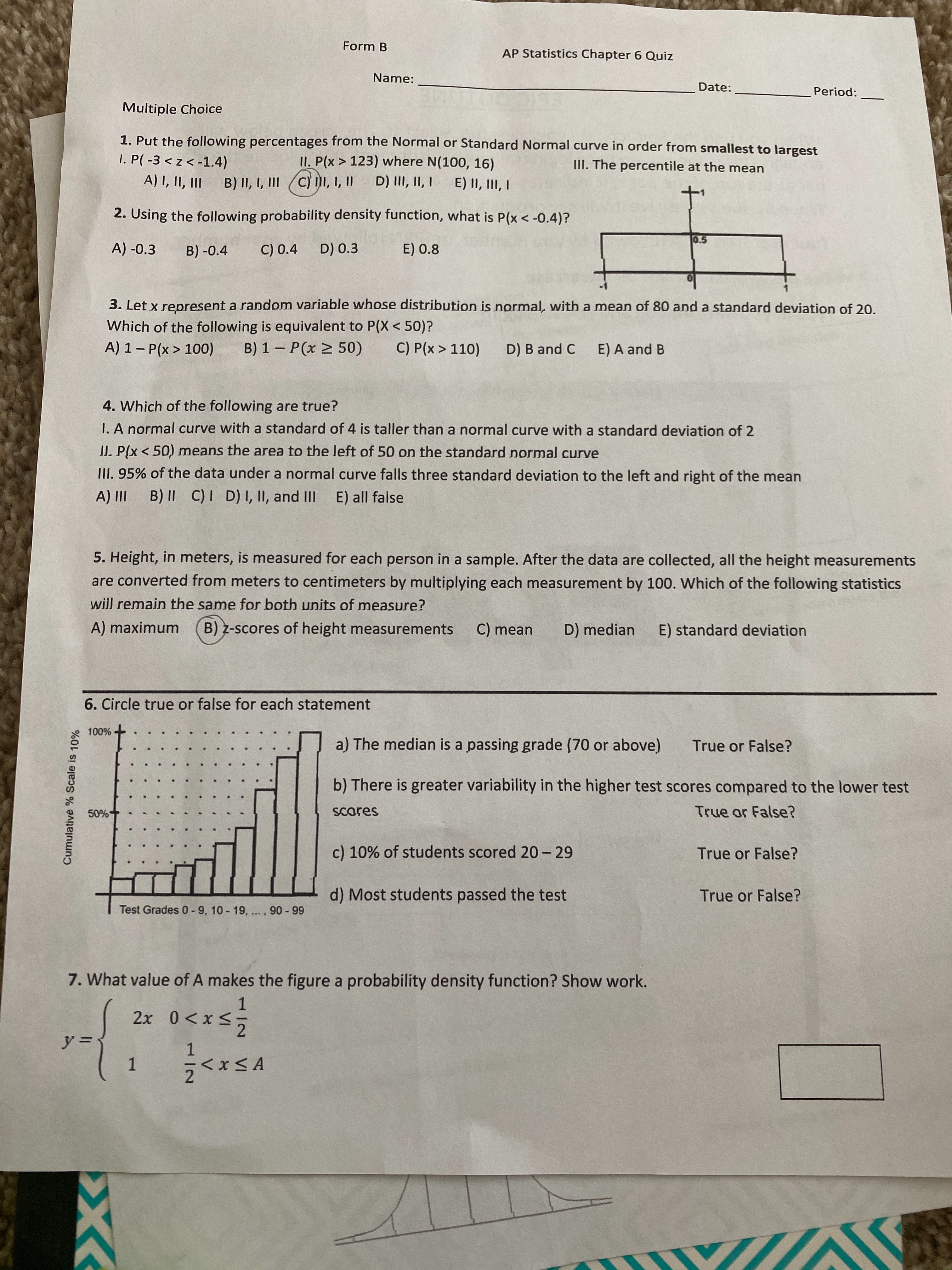


Answered 1 Put The Following Percentages From Bartleby



Business Statistics Ch 7 Flashcards Quizlet
コメント
コメントを投稿